Steam and gas turbines are crucial components in power generation, aviation, and various industrial applications. These machines are marvels of engineering that harness the power of steam or gas to produce mechanical energy efficiently. In this article, we will delve into the world of steam and gas turbines, exploring how they work, their applications, and the benefits they offer. You can also contact Allied Power Group if you are looking for the best steam and gas turbine.
The Basics of Steam Turbines
How do Steam Turbines Work?
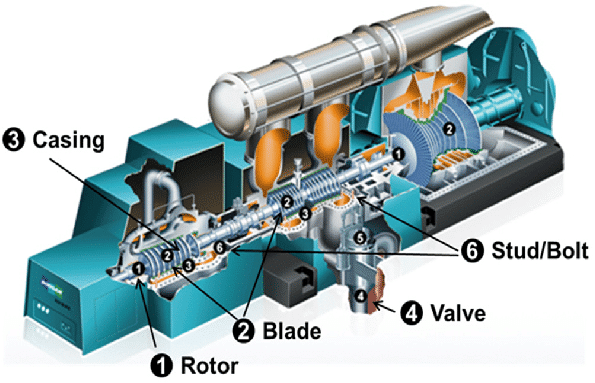
Steam turbines are devices that convert the thermal energy of pressurized steam into mechanical energy. The basic operation of a steam turbine involves the following steps:
- Steam is produced by boiling water using a boiler.
- The high-pressure steam flows into the turbine, where it expands and exerts force on the turbine blades.
- The force of the steam causes the turbine rotor to spin, converting the thermal energy into rotational mechanical energy.
- The rotational motion of the turbine rotor is used to drive a generator, producing electricity.
Applications of Steam Turbines
Steam turbines are widely used in power plants for electricity generation. They are also utilized in marine propulsion systems, where they power the propulsion shaft of ships. Other common applications of steam turbines include:
- Industrial processes such as steam-driven pumps and compressors.
- Cogeneration systems for simultaneous production of electricity and heat.
- Geothermal power plants that utilize steam from beneath the earth's surface.
The Wonders of Gas Turbines
Operating Principles of Gas Turbines
Gas turbines, also known as combustion turbines, operate on the principle of converting the energy of fuel combustion into mechanical energy. The operation of a gas turbine can be summarized as follows:
- Air is drawn into the compressor of the gas turbine and pressurized.
- The pressurized air is mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustion chamber, producing hot, high-pressure gas.
- The hot gas expands through the turbine, causing the turbine blades to rotate and generate mechanical energy.
- The rotational energy is used to drive a generator for electricity generation or propel aircraft in the case of aviation gas turbines.
Advantages of Gas Turbines
Gas turbines offer several advantages over other types of power generation technologies. Some of the key benefits of gas turbines include:
- High efficiency: Gas turbines can achieve high levels of efficiency in converting fuel into electricity.
- Quick start-up and shutdown: Gas turbines can be started and stopped rapidly, making them suitable for meeting fluctuating power demands.
- Low emissions: Gas turbines produce lower emissions of pollutants such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides compared to other fossil fuel-based power plants.
- Modular design: Gas turbine power plants can be easily expanded by adding additional units, allowing for flexible capacity growth.
Comparing Steam and Gas Turbines
Efficiency and Performance
Both steam and gas turbines are highly efficient in converting thermal energy into mechanical energy. However, there are some key differences in their performance:
- Steam turbines are typically more efficient at converting thermal energy into mechanical energy than gas turbines.
- Gas turbines have a higher power-to-weight ratio and can achieve quicker start-up times compared to steam turbines.
Applications and Flexibility
When it comes to applications and flexibility, steam and gas turbines have their unique strengths:
- Steam turbines are well-suited for large-scale power generation in stationary plants.
- Gas turbines are preferred for aviation and mobile power generation due to their compact size and quick start-up capability.
Conclusion
Steam and gas turbines are remarkable engineering marvels that play a vital role in power generation, transportation, and industrial processes. These machines have revolutionized the way we harness energy from steam and gas, offering efficiency, flexibility, and environmental benefits. By understanding the working principles and applications of steam and gas turbines, we can appreciate the significance of these technologies in powering our modern world.